The Quaternary Structure of Hemoglobin Contains
This tutorial will use hemoglobin and myoglobin to illustrate some general aspects of secondary tertiary and quaternary structure in proteins. The time evolution of these two bands is monitored after deoxygenation of encapsulated oxyhemoglobin obtained by diffusion of a reducing agent into the porous silica matrix.

Hemoglobin Facts Structure Summary Synthesis Function
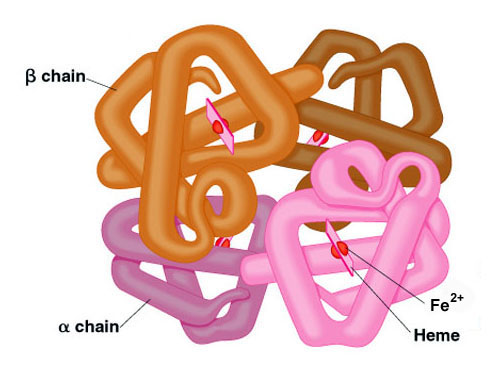
Adult hemoglobin is made of two alpha globin and two beta globin polypeptides.
. Here we demonstrate that the quaternary structure of tetrameric human normal adult carbonmonoxy-hemoglobin can readily be determined in solution at near-physiological conditions of pH ionic strength and temperature by NMR measurement of 15 N-1 H residual dipolar couplings in weakly oriented samples. The quaternary structure of hemoglobin contains - Six subunits - Four subunits - Two subunits - Eight subunits. Primary - amino acid sequence.
The quaternary structure of hemoglobin includes the assembly of two α and two β subunits each containing a heme group that is essential for oxygen binding. Hemoglobin represents a protein that possesses a quaternary structure. Each subunit of the hemoglobin contains a heme group that binds oxygen.
5 rows Hemoglobin has a quaternary structure. Quaternary Structure Bonds A protein with a quaternary structure is composed of several complex subunits. Hemoglobin heme groups shifting the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve to the left.
A variety of bonding interactions including hydrogen bonding salt bridges and disulfide bonds hold the various chains into a particular geometry. On mild treatment with urea haemoglobin partially dissociates but 𝜶𝝱 dimers remain intact. Quaternary structure adds stability by decreasing the surfacevolume ratio of smaller subunit Simplifies the construction of large complexes viral capsids are often composed of multiples of 60 proteins 20s subunit of proteosomes contain four heptameric rings 4 x 7 28 subunits Hepatitis B virus.
Major examples include insulin hemoglobin and most enzymes. Hemoglobin has a quaternary structure. There are 141 and 146 amino acids in the α and β chains of hemoglobin respectively.
The binding of oxygen to one sub unit increases the affinity of the other sub units for oxygen cooperativity. If the final protein is made of two subunits the protein is said to be a dimer. Many proteins require the assembly of several polypeptide subunits before they become active.
Which of the following statements best describes the shape and location of the heme groups. So Quaternary strucrure of hemoglobin consist of Two pairs of different protiens Named as Alpha and Beta. Quaternary - homo or hetero subunit interactions hemoglobin consists of 2.
It consists of two pairs of different proteins. In the quaternary structure the subunits are held together by the same interactions that stabilize tertiary structures such as hydrogen bonds salt bridges disulfide links and hydrophobic interactions between R groups. In the quaternary structure there is a strong interaction between 𝜶 and 𝝱 subunits.
It contains iron in the centre of the porphyrin ring. The quaternary protein structure involves the clustering of several individual peptide or protein chains into a final specific shape. Comparison with myoglobin enables us to assign them to quaternary structure relaxations.
Sperm whale myoglobin consists of 153 amino acids Mw 17199. Quaternary structure of hemoglobin with labeled subunits. Protein quaternary structure may involve both noncovalent and covalent forces.
It consists of two pairs of different proteins designated the α and β chains. The hemoglobin contains one heme per 18-19 000 g protein. These prosthetic groups are required for carrying oxygen in the blood.
Consisting of four subunits hemoglobin is responsible for binding oxygen in red blood cells. Single chain proteins end at this step. The structure is found to be a dynamic.
Characteristic spectral shifts are observed. Electron microscope observations show a ten-membered ring structure measuring 200 A in diameter. Alpha contains 141 amino acids while Beta contains 146 amino acids.
DNA and hemoglobin are examples of proteins that have a quaternary structure. Secondary - protein folds a helix and B sheet Tertiary - naivefully folded polypeptide. Quaternary structure is the interaction of two or more folded polypeptides.
Each subunit contains one non-protein heme group complexed to an oxidized iron atom Fe2. Sol 1. The amino acid composition of the pigment is reported.
As in myoglobin each subunit is. Heme group It is an iron-containing prosthetic group which is attached to each polypeptide chain. It serves as an oxygen reservoir picking up O2 from the hemoglobin and delivering it to the cells as O2 is used up in metabolism.
Up to 10 cash back Hemoglobin is a classic example of protein with a quaternary structure. Hemoglobin Quaternary Structure Here the four Hb subunits are shown. If three subunits must come together the protein is said to be a trimer.
Double-click on one of the gray heme group atoms in the model above and zoom in to examine it. The Two identical Alpha chains And the two identical Beta chain View the. The predilection for the globus pallidus may relate to hypotensive effect of CO poisoning in the watershed territory of the arterial supply.
The quaternary structure of a hemoglobin molecule includes four tertiary structure protein chains which are all alpha helices. The hemoglobin molecule thus formed is composed of four subunits and thus is called a tetramer. It is proposed that Helisoma hemoglobin consists of a 17-106 dalton circular assembly of ten 175-200 000 dalton polypeptide chains.
Describe the levels of protein structure. Four subunits make up a.

The Quaternary Structure Of Hemoglobin And Its Oxygen Carrier Heme Download Scientific Diagram

Comments
Post a Comment